As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases
Understanding “Squat Eccentric vs. Concentric” is key to maximizing your workout results. The eccentric phase focuses on muscle elongation and strength, while the concentric phase enhances muscle shortening and power. Discover how balancing both can boost your fitness progress.
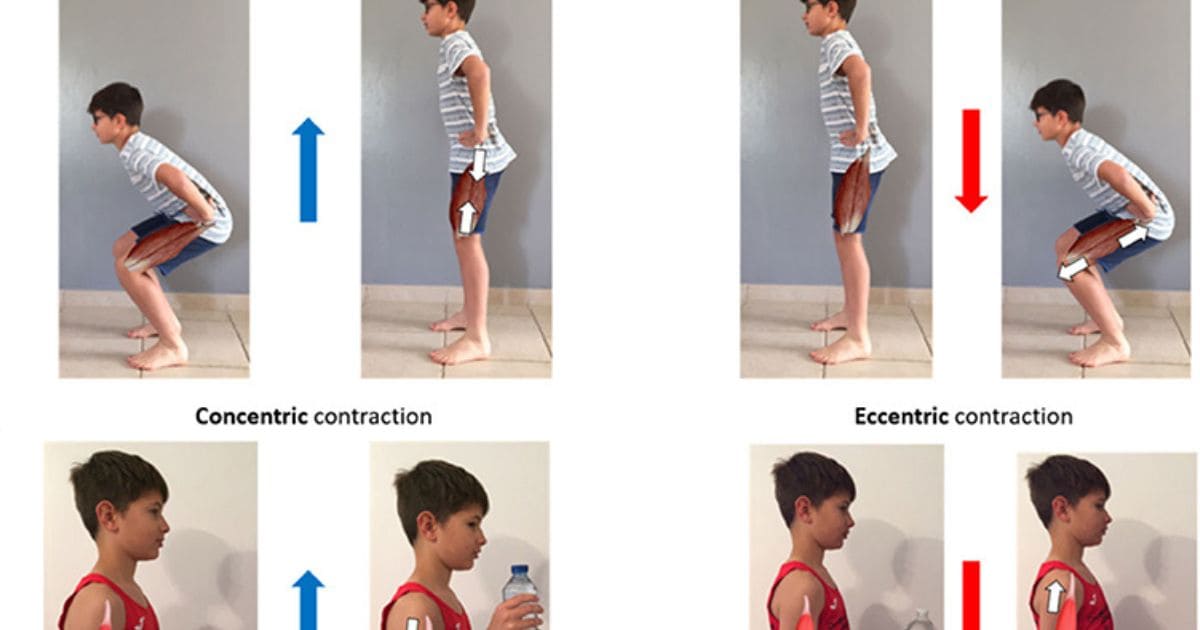
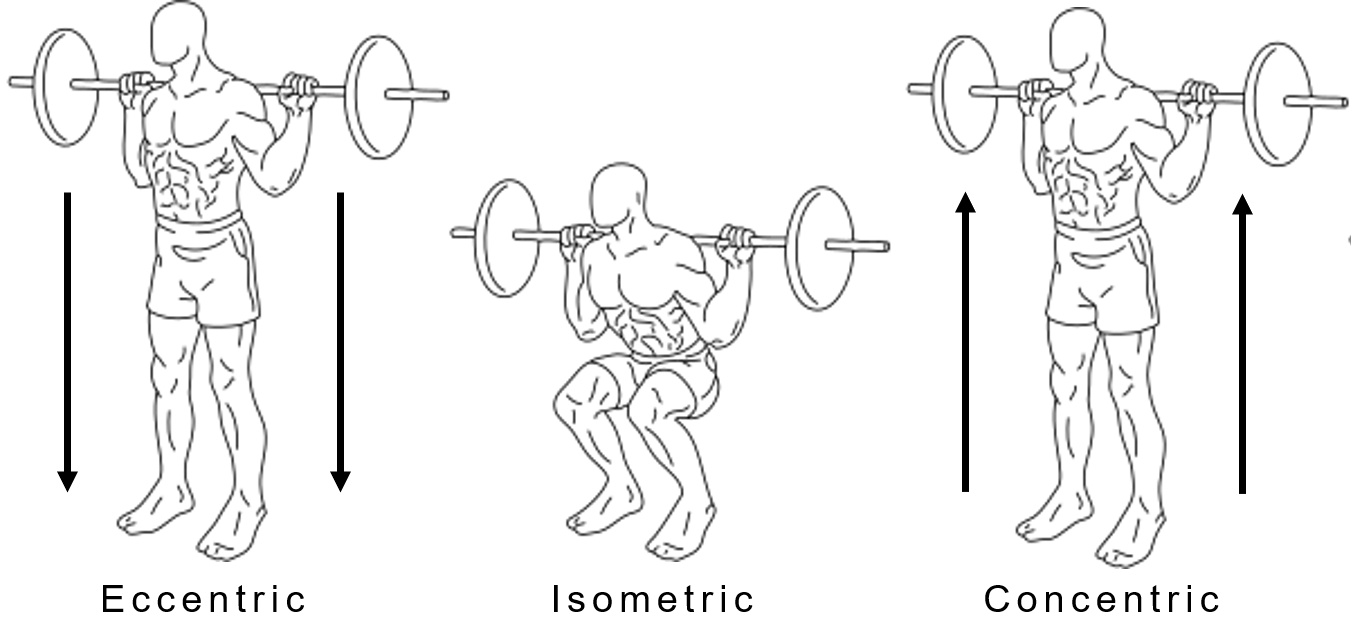
Squats are a fundamental exercise in strength training, with eccentric and concentric phases playing crucial roles in muscle development. The eccentric phase involves lowering the body, lengthening the muscles, and creating tension. On the other hand, the concentric phase is when you push your body back up, shortening the muscles and generating force.
The key to maximizing muscle growth, improving strength, and enhancing overall performance is to focus on both phases during squats. We will delve deeper into the differences between squats’ eccentric and concentric phases and how they contribute to your fitness goals.
Muscle Engagement
Engaging muscles differently, squat eccentric focuses on lowering while squat concentric emphasizes pushing upwards. These movements activate muscles uniquely for strength gains and muscle development.
Squats are a popular exercise that can help build strength and muscle mass. However, did you know how you perform squats can significantly affect muscle engagement? The eccentric and concentric phases of the squat activate different muscles at different levels.
Eccentric Phase
The eccentric phase of the squat refers to the lowering phase of the movement when you are bending your knees and lowering your body towards the ground. During this phase, the muscles are lengthening under tension, which can lead to muscle damage and soreness.
However, this phase also allows for greater activation of certain muscles, such as the quadriceps and glutes. To maximize muscle engagement during the eccentric phase, it’s important to focus on controlling the descent of the squat. Additionally, incorporating pauses or holds at the bottom of the squat can increase time under tension and further enhance muscle activation.
Concentric Phase
The concentric phase of the squat refers to the upward phase of the movement when you are pushing through your legs and extending your knees to stand up. During this phase, the muscles are shortening under tension, which can lead to greater force production and power. However, this phase may not activate certain muscles as much as the eccentric phase.
Use proper form and drive through the heels during the concentric phase to activate your glutes and hamstrings. Additionally, incorporating explosive movements or plyometrics, such as jump squats, can increase force production and enhance muscle activation. You can, however, tailor your squatting technique to target specific muscles and achieve your fitness goals by understanding the different muscle engagement during each phase.
Mechanics And Form Squat Eccentric Vs Concentric
Understanding the mechanics and form of “Squat Eccentric vs. concentric” is essential for maximizing muscle growth and strength. Proper technique in both phases ensures effective workouts and minimizes injury risk.
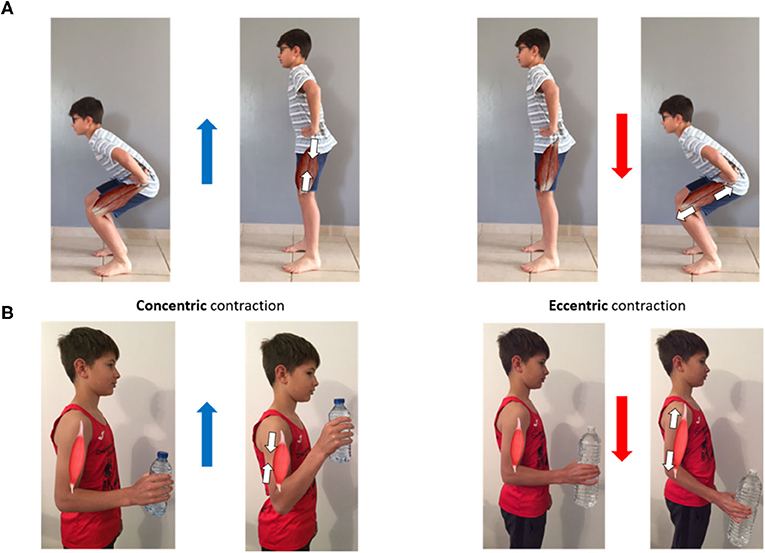
When mastering the mechanics and form of squat movements, understanding the differences between eccentric and concentric movements is crucial. Both eccentric and concentric movements play a vital role in optimizing the effectiveness of squats, and comprehending their mechanics can greatly enhance your performance.
Eccentric Movement Mechanics
The eccentric phase of a squat occurs when the muscles lengthen under tension, typically during the lowering portion of the movement. As the body descends into the squat, the quadriceps and glutes are engaged to control the movement.
Strength and stability are built by lengthening muscles while generating force. Maintaining proper form during the eccentric phase is crucial to minimize the risk of injury and maximize the benefits of the exercise.
Concentric Movement Mechanics
During the concentric phase of a squat, the muscles shorten under tension as the body rises back to the starting position. The quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes are primarily engaged during this phase to propel the body upward. Maintaining proper form during the concentric phase is essential for maximizing the power output and reaping the full benefits of the exercise.
Muscle Growth
Impact Of Eccentric Training
Eccentric training focuses on the lengthening phase of the muscle contraction.
Impact Of Concentric Training
Concentric training emphasizes the shortening phase of muscle contraction.
Strength Gains
Strength Gains: Squat eccentric and concentric movements offer unique benefits for enhancing strength.
Eccentric Strength Benefits
Eccentric squat movements involve lowering the weight, emphasizing muscle lengthening and control.
Increased time under tension leads to muscle hypertrophy.
Enhances muscle strength through a controlled lowering phase.
Concentric Strength Benefits
Concentric squats involve lifting the weight, focusing on muscle contraction and power.
- Improves explosive strength and power output.
- Enhances overall muscle recruitment and force production.
Injury Prevention
Understanding the differences between eccentric and concentric training is crucial to preventing injuries during exercise. Each type of training offers unique benefits for injury prevention, and incorporating both into your workout routine can help you maintain a balanced and resilient body. Let’s delve into how eccentric and concentric training can contribute to injury prevention.
Eccentric Training And Injury Prevention
Eccentric training involves lengthening a muscle under tension, which can help prevent injuries by improving muscle strength, flexibility, and control. This type of training focuses on the lowering phase of an exercise, such as the downward motion of a squat. By emphasizing the eccentric phase, you can build resilience in your muscles and joints, reducing the risk of strains and tears.
Concentric Training And Injury Prevention
In contrast, it involves shortening a muscle under tension, which can also prevent injuries. This type of training enhances muscle power and explosiveness, contributing to overall stability and reducing the risk of sudden injuries. Incorporating concentric movements, such as the upward phase of a squat, can help improve your ability to generate force and maintain proper form during various activities.
Training Techniques
When training techniques, the squat eccentric and concentric movements play a crucial role in building strength and muscle. The eccentric phase focuses on the lowering portion of the squat, while the concentric phase emphasizes the upward movement.
Both are essential for maximizing muscle activation and overall performance in strength training.
Squats are one of the most popular exercises for building lower body strength. However, not all squats are created equal. Squat eccentric and concentric training techniques are two different approaches to building strength.
Effective Eccentric Training Methods
The eccentric phase of a movement is focused on during eccentric training. You lower your body to the ground during this part of the squat. Eccentric training lets you lift more weight than concentric training alone. Some effective eccentric training methods include:
- Negative reps: This involves lowering the weight slowly and controlled for 3-5 seconds.
- Paused reps: This involves pausing at the bottom of the squat for a few seconds before standing back up.
- Drop sets: This involves performing a set with a heavy weight, then immediately dropping the weight and performing another set with a lighter weight.
Effective Concentric Training Methods
Concentric training is effective because it allows you to build explosive strength and power. Some effective concentric training methods include:
- Speed reps: This involves performing the concentric phase of the squat as explosively as possible.
- Jump squats: This involves jumping explosively out of the squat position.
- Resistance band squats: This involves using resistance bands to add extra resistance to the concentric phase of the squat.
Incorporating eccentric and concentric training techniques into your training program can help you build strength and power. Experiment with different methods and find what works best for you. Remember to always focus on proper form and technique to avoid injury.
Application In Workouts
When incorporating squat eccentric and concentric training into your workouts, understanding the application of each is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your exercise routine.
Incorporating Eccentric Training
Eccentric training, also known as negative training, involves focusing on the lowering phase of the squat movement. This type of training creates greater muscle tension and is effective for muscle growth and strength gains. To incorporate eccentric training into your workouts, you can:
- Focus on slowing down the lowering phase of the squat movement
- Use a heavier weight during the lowering phase to increase the eccentric load
- Perform eccentric-only squats using a controlled descent and assistance for the ascent
Incorporating Concentric Training
Concentric training, on the other hand, emphasizes the lifting phase of the squat movement. This type of training is essential for developing explosive power and improving overall muscle function. To incorporate concentric training into your workouts, you can:
- Focus on explosive movements during the lifting phase of the squat
- Incorporate plyometric exercises such as jump squats to enhance concentric power
- Use lighter weights to perform explosive concentric squats
Conclusion
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases